


Committed to Sustainable Cities and Human Settlements for All

In Special Consultative Status with ECOSOC
Abstract: Greening, ecology, and low carbon are concrete embodiment of sustainable development in cities and the ultimate direction of urban development across the world. The construction of green eco-cities is conductive to urban transformation in the world, and is of great significance for improving the quality of urban construction. Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark is a world-class high-end ecological technology research & development zone. Upholding a philosophy of "improving life via eco-orientation and wisdom, elevating quality through openness and integration" and focusing on the vision of "pastoral environment, green development, and good life", the park has been committed to ecological, green and sustainable development, and is endeavoring to build an integrated city-industry district characterized by ecology, intelligence, and openness.
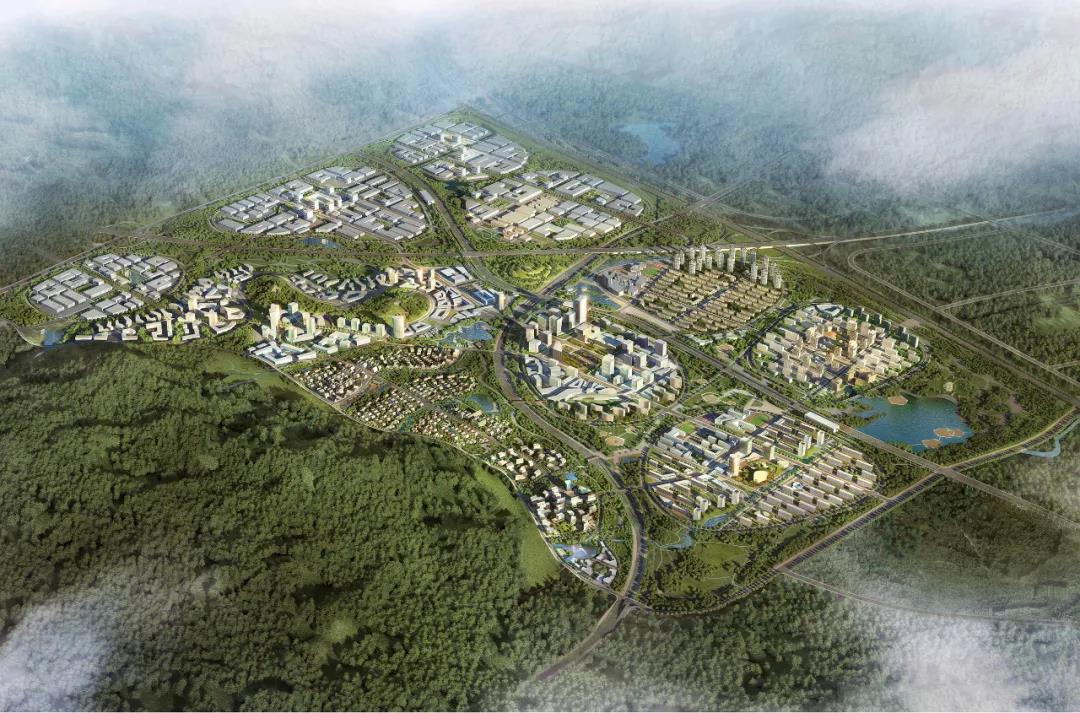
Figure 1: Planning Map of Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark
1. About the Park
1.1 Background
In July 2010, the Ministry of Commerce of the People's Republic of China
(MOFCOM) and the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy of Germany
(BMWi) signed the Memorandum of Understanding on Joint Support for the
Establishment of the Sino-German Ecopark, as a bid to support the establishing
of the Sino-German Ecopark in Qingdao Economic and Technological Development
Zone. The site selection for the park was completed in March 2011 and the
foundation was laid in December of the same year. In May 2012, the Commission
Office for Public Sector Reform of Qingdao City issued the Reply on
Establishing the Management System of Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark, and decided
to set up the Management Committee of Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark. In July
2013, the Qingdao Municipal Government adjusted the management systems of
Qingdao West Coast New Area and related functional areas, and decided to
establish the Management Committee of Qingdao International Economic
Cooperation Zone (listed as the Management Committee of Qingdao Sino-German
Ecopark) as an agency of the Qingdao Municipal Government.
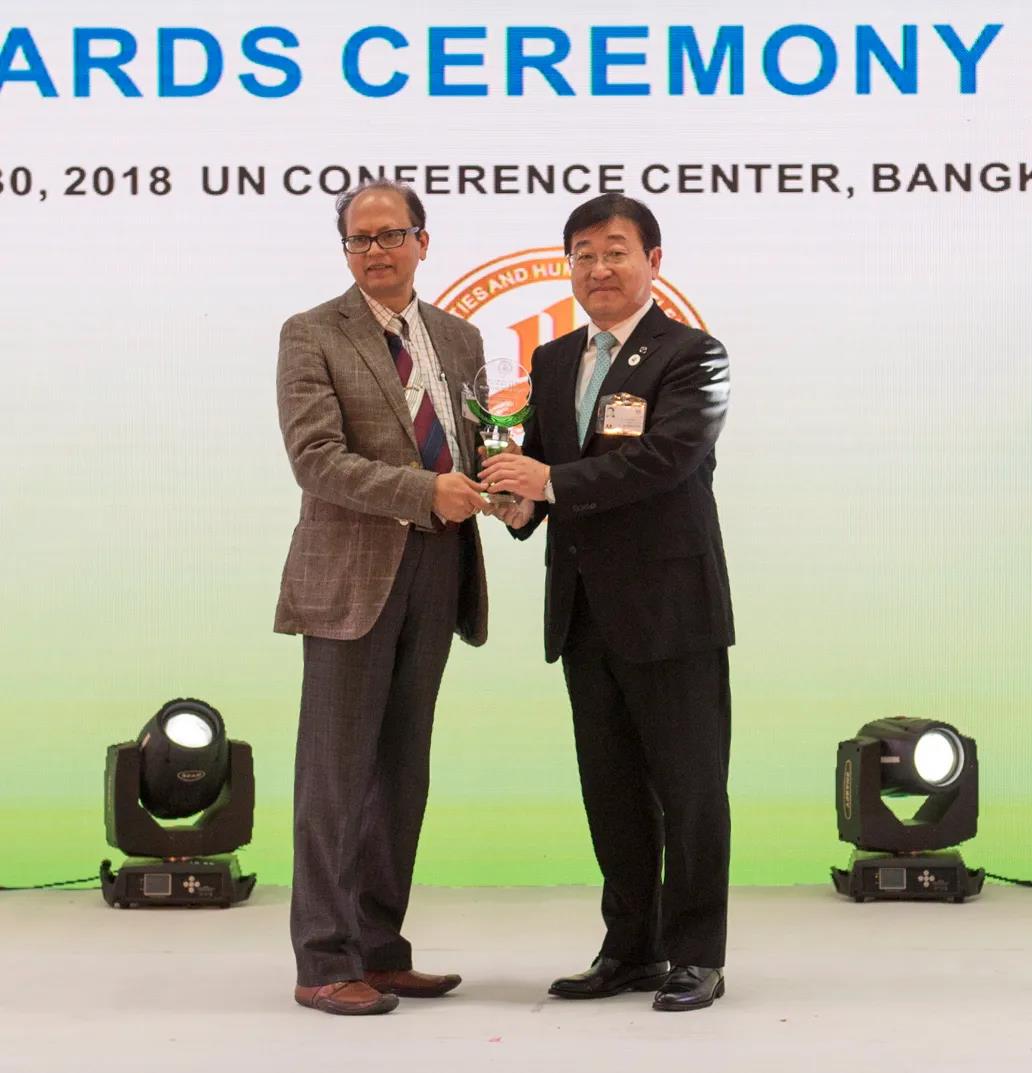

Mr. Choudhury
Mohanty, Coordinator of Environment Programme, UNCRD/UN DESA
presented the
“Global Green District” award to Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark, October 2018,
UN
Conference Center, Bangkok, Thailand
Photo credit by @ GFHS
1.2 Overview
Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark is located in Qingdao, China, facing South Korea, Japan, and North Korea across the sea. With a superior sea, land, and air transportation system, it is an important window for Qingdao to open to the outside world, especially to Germany. The initial area has been extended to 34.92 km2 from the planned 11.6 km2, and the future area is planned to cover 202 km2.
Since the establishment, the park has adhered to the development vision of "pastoral environment, green development, and good life" and fully implemented new urbanization, ecological civilization, and the guidelines of Central Urban Work Conference. With fruitful results, the construction of the park has been highly valued by Chinese and German governments and all walks of life, setting up a model to lead the sustainable development of future cities in China or even in the world.
The park has been awarded honors such as one of “the First Batch of National Low-carbon City (Town) Pilots” and one of “the First Batch of National New Energy Demonstration Parks” granted by the National Development and Reform Commission, the “National Smart City Pilot”, “National Green Ecological Demonstration Urban Area” and the “Chinese Habitat Environment Award” by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development, “National Green Manufacturing International Innovation Park” by the Ministry of Science and Technology, “Sino-German Intelligent Manufacturing Lighthouse Park” by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, and the “First National Comprehensive Standardization Demonstration Park” by the Standardization Administration. In 2017, the park was awarded the “China's Top Ten Industry-City Integration Classic Cases”, and won the “Global Green Park” of “Sustainable Cities and Human Settlements Awards” in 2018, and the “Sino-German Ecological Demonstration Urban Pilot Area”, “China Smart Park” and other honorary titles in 2019, and officially became a member unit of the National Economic and Technological Development Zone Green Development Alliance in 2019. The development and construction of Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark has been highly valued by the Chinese and foreign governments and praised by the industry. The park is mentioned for many times during the mutual visits of the leaders of China and Germany.
2. Natural Ecology and Environmental Protection
Biodiversity is of great significance to the sustainability of urban ecosystem functions. With regard to natural ecology and environmental protection, the park protects both habitats and native species. In addition, it identifies core ecological resources and builds an ecological security pattern to ensure biodiversity.
2.1 Protection of Biological Habitats
The flora and fauna resources of the park are mainly distributed in the
mountainous area where the southern Laojunta Mountain, Niuqi Mountain, and
Beiling Mountain are located, as well as in the wetlands such as Zhuguo
Reservoir, Heluobu Reservoir, Longquan River, Shanlong River and Shanwang
River. Firstly, the park has enhanced the protection of forest resources by
repairing damaged ones, speeding up restoration and replanting, and by
increasing canopy density and coverage, thus ensuring that the habitats are not
interfered and invaded. Secondly, the park has enhanced the protection of
wetland resources by renovating the water ecological environment, controlling
the discharge of pollutants, and by preventing water pollution incidents. It
has also built green belts on the river banks to protect water ecology and
ensure the intact of habitats, as shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2: Bird Inhabits

Figure 3: View of Green Space
2.2 Protection
of Native Species
The park focuses on the protection of native plants by giving priority to native species for green space construction and by identifying those with high ornamental value. In the ecological green space restoration and urban green space system construction, native species are preferred to ensure the proportion of them in the planning area. With the existing dominant native species retained, species with high ornamental value were identified and used in green lands and riverside greenbelts to make those spaces more beautiful, as shown in Figure 3.
2.3 Establishment of Ecological Security Pattern
The park is establishing an ecological security pattern covering "one core, two zones, three centers, and multi-corridor": one core: Laojunta Mountain ecological green core; two zones: Zhuama Mountain and Jiaozhou Bay ecological zones; three centers: Zhuguo and Heluobu reservoirs, and Niuqi Mountain; multi-corridor: combination of water system, roads, gullies, and greenbelt. The details are shown in Figure 4. By connecting important points of ecological sources, the connection of resources and wildlife migration are ensured. Large migration corridors must have sufficient width, and the general ones should be 600m wide at least. The ecological corridors in the planning area are mainly divided into regional structural ecological corridors and internal optimized ones. Regional structural ecological corridors were constructed in Laojunta Mountain and Zhuama Mountain to provide ecological functions including habitat protection, biodiversity conservation, wind and sand prevention, and soil and water conservation. The width of such corridors is controlled within 800-1500 meters. Five internal optimized ecological corridors were constructed against Longquan River, Shanlong River, Shanwang River, Jiuqu River, and Beizhuang River to promote migration of small creatures and isolate noise. The width of such corridors is controlled within 50-100 meters.
3. Urban Planning and Construction
In this aspect, the first endeavor is to strengthen the top-level design for guiding park construction; the next step is to vigorously develop ecological construction and improve living and office environment; the third is to innovate the energy utilization mode to reduce energy resource consumption; in addition, the management system and mechanism of ecological construction has been innovated to ensure the effective implementation of all construction indicators.
3.1 Strengthening Top-level Design for Guiding Park Construction
Promoting City-industry Integration and Building
Pastoral Environment based on Scientific Orientation: The park, drawing on the German Rhine model,
comprehensively organizes the three major parts of production, life, and
ecology. Through the integration of industry and urban functions, it
scientifically sets the land proportions for industry, commerce, residence, and
afforest. The park makes every effort to build an ecological demonstration
district that is suitable for living and business, realize the
"city-industry integration and jobs-housing balance", and to shape an
idyllic environment with "mixed city and rural characteristics". It
makes people live and work in the city with complete facilities and a
high-quality life and enjoy the idyllic scenery at the same time.
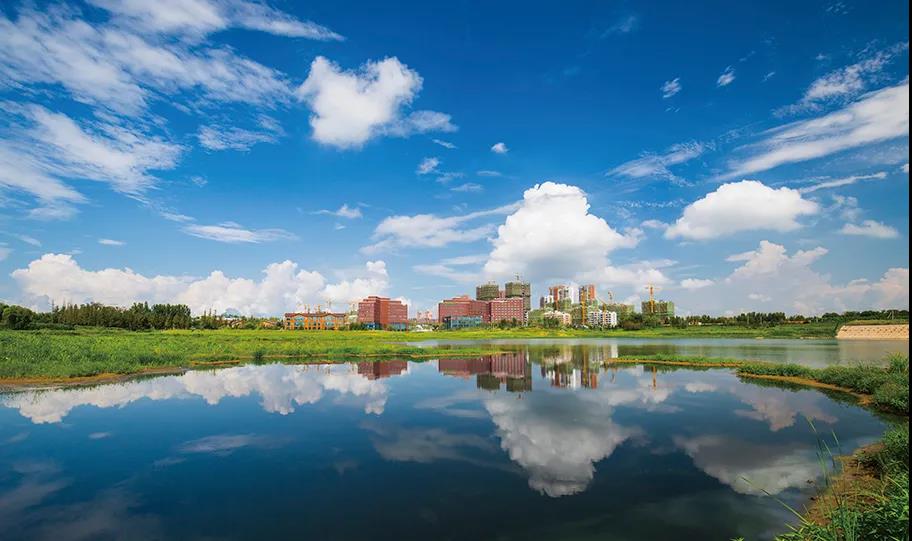

Figure 4: Landscape of Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark
Putting Standards beforehand and establishing the park based on Standards: The park has developed four indicator systems to lead the green low-carbon construction and to set a carbon emission limit before carrying out work. Over 20 indicators are related to the human settlements development. The park actively improves the connectivity of Chinese and German standards and participates in the establishment of national and industrial standards. So far, a green ecological construction standard system consisting of 16 parts has been established. TÜV NORD, Germany's largest evaluation agency, has confirmed that the standards of Sino-German Ecopark meet the practical requirements of sustainable development of the international ecopark and represent the advanced level of international ecopark construction standards.
In 2018, combined with the development practices and dynamic assessment of the park over the past six years, with reference to the United Nations 2030 Sustainable Development Goals, the New Urban Agenda and other standards, the original ecological indicator system was improved to form the Sino-German Ecological Park 2030 Sustainable Development Indicators System, and formulated the ecological indicators version 2.0 to meet the latest requirements of sustainable development practices and represent the first-class level of the international ecological park.
Relying on Planning for Guidance and Control: By introducing internationally advanced philosophy of planning and design, the park has developed the standards of park master planning, regulatory planning, and planning in 37 aspects including industry, transport, municipal administration, energy, green building, and others at a high level. The philosophy of ecological, low-carbon and smart construction is fully implemented in the regulatory planning of the park to maximize the resource and energy conservation and environmental protection and to promote the sustainable construction of the park.
Promote “multiple plannings in one”: Delimit and strictly abide by the three control lines of ecological protection red line, permanent basic farmland, and urban development boundary, and determine the binding indicators for urban construction, with 30% for residential land, 30% for production land, and 40% for ecological land, strengthen the original ecological protection, ensure that the proportion of original landscape and texture protection is ≥ 40%, and the plant proportion of bird feeding trees is ≥ 30%, and incorporate control indicators into regulatory planning.
3.2 Developing Ecological Construction to Improve Living and Office Environment
Promoting Green Energy-saving Buildings: On the basis of fully implementing the national
standards, mandatory 100% green buildings and 100% green construction,
vigorously promote prefabricated buildings, large-scale application of German
passive house technology, and actively introduce DGNB standards. At present,
4.2 million square meters of green buildings are under construction, and the
proportion of buildings meeting 2-star standard or above has reached 60%. The
C2 group is the first Asian project to achieve the DGNB Urban District
Certification. In 2015, German Enterprise Center, the first largest building
wining Germany's DGNB Platinum Award in Asia, was completed and Modular Freight
Container Apartment, the first pilot project of prefabricated buildings, was
launched; 2016 witnessed the completion of the Qingdao Passive House Technology
Experience Center, the largest PHI-certified Passive House Public Building in
Asia, and the first Asian Passive House Conference was held in the same year. A
total of 300,000 square meters of passive ultra-low energy buildings have been
built, which are widely used as offices, residences, apartments, schools,
kindergartens and so on.
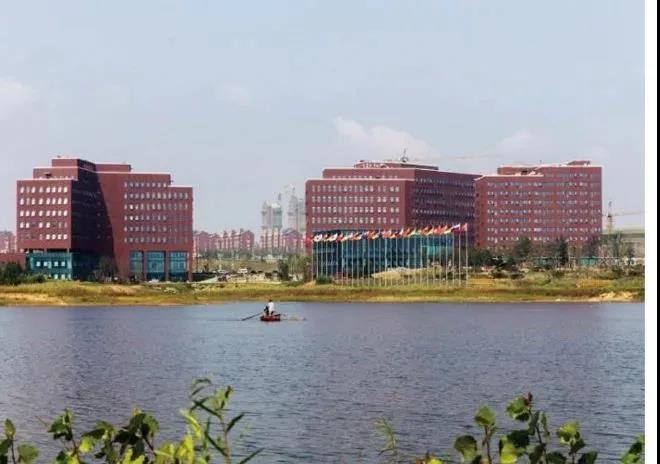

Figure 5: German Enterprise Center
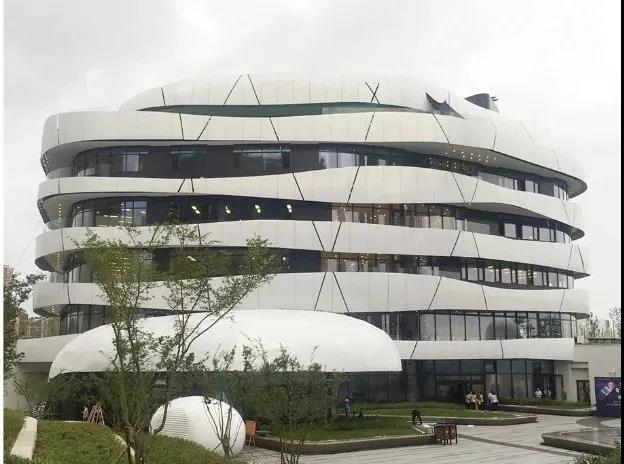

Figure 6: Passive House Technology Experience Center
Advancing Sponge City and Green Municipal Construction: Based on resource protection and ecological construction requirements, 300,000 square meters of environmental greening restoration and upgrading and 100,000 square meters of bare soil coverage projects were completed, and the first "Sponge City Construction Management Measures" in the province was issued, and the first permeable and noise-reducing municipal road in the province was built, with an annual surface runoff control rate more than 75% and a core area of 84%. Vigorously promote the modular treatment of sewage and reuse of reclaimed water to realize the recycling of water resources. Actively promote garbage classification, recycling and treatment to achieve solid waste reduction, harmlessness, and recycling. Four sponge city demonstration projects were completed, with a permeable pavement area of 16,000 square meters, a permeable pipeline laying of 2,600 meters, and a sponge city area of 300,000 square meters. Simultaneously promote the construction of park systems including public leisure parks, urban farms, corner parks, pocket parks and others to build a beautiful park city.
Promoting Green Transportation: The park is dedicated to strengthening green public transportation and green mobility, achieving seamless connection between different transportation modes, and vigorously building a multi-level, three-dimensional convenient transportation system. The park actively provides a parking lot and leasing facilities for bicycles, completely uses new energy buses, and ensures that more than 20% (included) of the parking spaces in the communities will be equipped with charging piles. The minibus system has been built in the park. The density of bus lines reaches 3.2km/km2. There are bus lines passing through every community and bus service facilities within an average radius of 500 meters. The system guarantees that people can walk to a bus station within 5 minutes. The park also advocates a green mobility mode to minimize the energy consumption of the transportation system, realize a mobility mode dominated by the slow trip, and to establish the dominant position of public transportation in motorized mobility.
Shaping A Smart City Platform: The park actively promotes the construction of a smart city to create
an ecological city, improves the efficiency and effectiveness of ecological
construction management, and has built eight intelligent projects such as the
park's geographic information system and environmental monitoring system. The
park is committed to implementing the concept of nationwide sharing and taking
the lead in building a smart community to settle 2,800 households for carrying
out demolition and reconstruction projects,and has realized a new lifestyle
guided by the concept of ecology and low carbon.

Figure 7: Picture of Fu Lai Community
3.3 Reducing Energy Resource Consumption by Innovating Energy Utilization Mode
For energy supply within the park, a distributed ubiquitous energy net system is used to make full use of renewable energy and clean energy. The park adopts a combination of a centralized system and distributed system, mixed and independent systems to optimize the energy system design from energy production, storage & transport, application and regeneration and reasonably allocate various energy and resources. The renewable energy utilization rate can reach more than 33%.
3.4 Ensuring Effective Implementation of Various Indicators by Innovating Ecological Construction Management System and Mechanism
Giving full play to the advantage of "super-department system" by optimizing organizational structure: The "horizontal" management system in the planning and construction field has been broken to integrate the approval authority assumed by the original 8 functional departments in the area under their jurisdiction into one department for implementation. Related work in the original 16 district departments have been pairing coordinated by the depatment to eliminate and lessen departmental conflicts. Parallel examination and approval have been implemented to realize information sharing and seamless connection, promoting fulfillment of the responsibility to achieve green ecological construction goals and management efficiency improvement.
Establishing Green Ecological Construction Research Institute: Green Ecological Construction Research Institute of Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark has been established to review green ecological construction of the settled projects, ensuring full implementation of the indicator systems in the park. The development of green ecological industry or direction of ecological construction in the park has been accelerated or controlled, providing strong intellectual and technical supports for ecological demonstration park nationwide and even worldwide.
Establishing green ecological management mechanism: The technical system related to green ecology and
low-carbon has been formulated, including indicator system, management method,
design & construction & operation guidelines. According to requirements
of the technical system, the technical review and control on the whole process
(totally seven phases from investment negotiation to operation management) has
been implemented to ensure the comprehensive fulfillment of green, ecological
and low-carbon related indicators in the park.
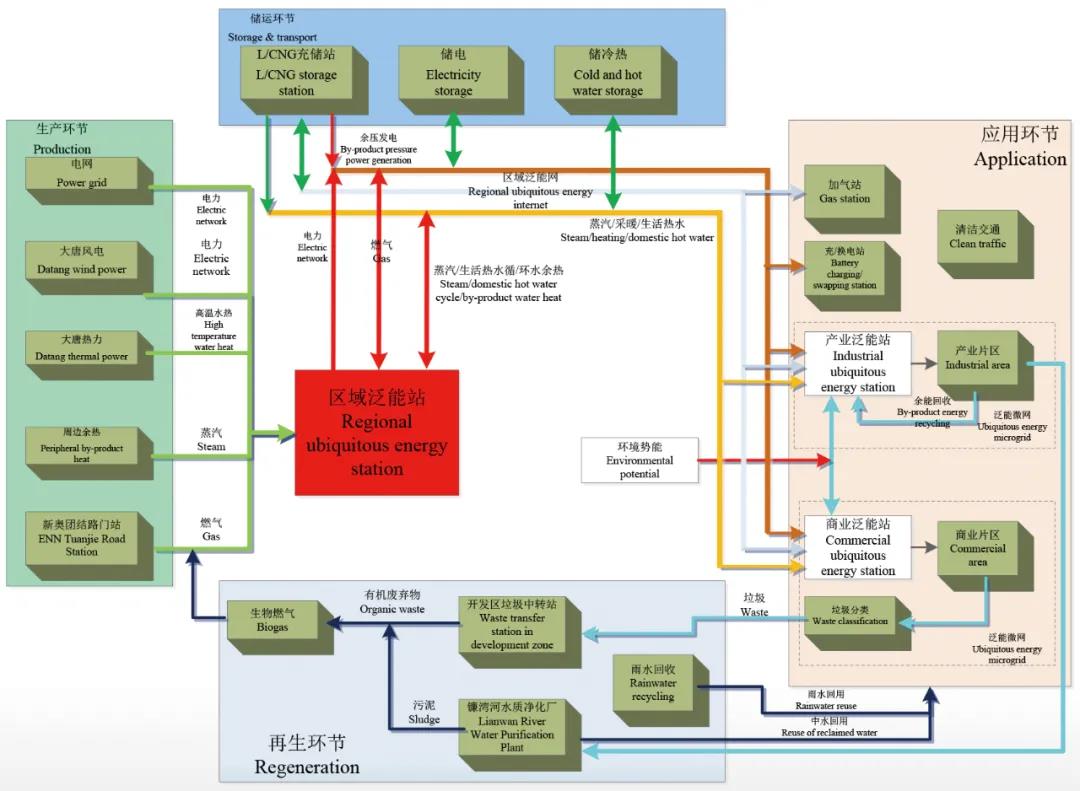
Figure 8: Four Steps of Energy Supply for Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark
4. Achievements
4.1 Obvious Building Energy-saving Effect
Since the commencement, energy-saving in the park has been implemented effectively through low-carbon ecological construction, preliminarily indicating the demonstration effect. It is estimated that after the completion of the distributed energy system, the energy consumption of per RMB 10,000 GDP in the park will reach 0.23t (standard coal), reducing carbon emissions by 790,500 t/year, with clean energy utilization of 84.6%, renewable energy utilization of 20.6%, comprehensive energy-saving rate of 50.7%, and carbon emission reduction rate of 64.6%. The energy-saving rates of the completed Passive House Technology Center of Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark and German Enterprise Center are over 90% and 80% respectively, with total carbon emission reduction of about 6,344 t/year, indicating the obvious energy-saving effect. The energy consumption per unit GDP and carbon emission intensity of the park have reached that of the developed countries. The key performance and low-carbon practice studies of Siemens’ sustainable urban development show that the park’s per capita carbon emission intensity in 2020 will be lower than the average level of developed countries, reflecting the demonstration significance of the successful cooperation between the Chinese and German governments in urban areas.
4.2 Effective Protection and Improvement of Living Environment
The original mountains, water sources, woodlands, wetlands, villages and
history & culture of the park base are preserved and protected to the
maximum extent. Within the scope of construction, the area of small block has
been well planned to create the neighborhood center space; within the walking distance,
sound supporting public services are provided to enable residents undertaking
daily activities in neighborhoods. All above have optimized the living
environment of the original residential area, improving the residents' mobility
conditions, providing good jobs and high-quality education environment, and establishing
a habitat environment suitable for "mobility, living, education,
retirement, recreation, and shopping".

visited the Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark, November 2019, Qingdao, China
4.3 Establishment of Platform for International Industrial Cooperation
Since the official commencement in July 2013, this place has gradually developed from an suburban area without road, supporting facility, and enter into a park with more than 500 registered enterprises, including 6 Fortune Global 500 enterprises and over 30 international hidden champion enterprises. The park has received over USD 400 million of foreign investment and over RMB 6.5 billion of domestic investment. Enterprises from 16 countries and regions have invested and settled in the park, preliminarily established a "4 + N" modern industrial system represented by intelligent manufacturing, healthcare, new energy & new equipment, and passive houses, gathered more than 9,000 related talents, including 15 academicians, 2 full-time national talents, 196 doctors, 718 masters, 428 talents from Taiwan, Hong Kong and Macao as well as other countries.
4.4 Establishment of High-end and Environmental Protection Industrial Cluster
In terms of industrial selection, the park always adheres to the
following selection principle of industry: high technology, high productivity
and high contribution rate as well as low resource consumption, low carbon
emissions and low environmental impact. Intelligent manufacturing, building
industry with low energy consumption, high-end R&D, New energy vehicles and
supporting industries, biotechnology industry and other industries are
established in the park. The main projects are shown in the table below.

4.5 Realizing Organic Integration of Chinese Speed and German Quality
The park adheres to the principle of "taking a dominant place, learning helpful experience", giving full play to the advantages of Sino-German government cooperation platform, and improving the speed and quality of park construction projects. The park has introduced German enterprises into the Chinese market with the concept of "Germany +", promoting the transformation and development of domestic enterprises with the concept of "+ Germany", and attaching importance to the "German business philosophy, standards, technology and investment proportion". The park also has introduced dozens of world-renowned design consulting companies including German gmp, SBA, Obermeyer, and Energydesign to participate in the whole process of park construction, realizing the organic integration of Chinese speed and German quality and constructing a green ecological park with German standards and international characteristics.
5.
Conclusion
Since the commencement, Qingdao Sino-German Ecopark has made great achievements in urban development and low-carbon ecological construction. It has become a model of a new type of city displaying vigorous economy, energy conservation and ecological livability to the world. The innovative model of human settlements initiated here will spread to the whole country and even to the world, providing a model and guidance for the sustainable development of cities in China and even the world in the future.
Copyright © Global Forum on Human Settlements (GFHS)
