Committed to Sustainable Cities and Human Settlements for All
In Special Consultative Status with ECOSOC
Contribute to the Implementation of
Sustainable Development Goals and New Urban Agenda
--IGMC 3.0 Officially Released during
Habitat III
The International Green Model City (IGMC)
Standards 3.0 (hereinafter referred to as the "IGMC 3.0") was
released at the 11th Global Forum on Human Settlements (GFHS-XI) that took
place in Quito on 18 October 2016 as a parallel event of "Habitat
III". The relevant experts and senior representatives from GFHS,
UN-Habitat, UNEP and local governments attended the ceremony. IGMC 3.0 is an
assessment and planning guidance tool for sustainable urban development and
provides technical means and evaluation methods for the specific implementation
of the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda and the New Urban Agenda at local
and community levels.
Registering itself in the context of the
new emerging issues and policies as related to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable
Development, the Climate Change Paris Agreement and the New Urban Agenda, IGMC
3.0 aims to further contributing to the vision and transformative commitments
the global community agreed upon, and to further contributing to the
transformation the way cities are planned, developed, financed and operated
towards sustainability.
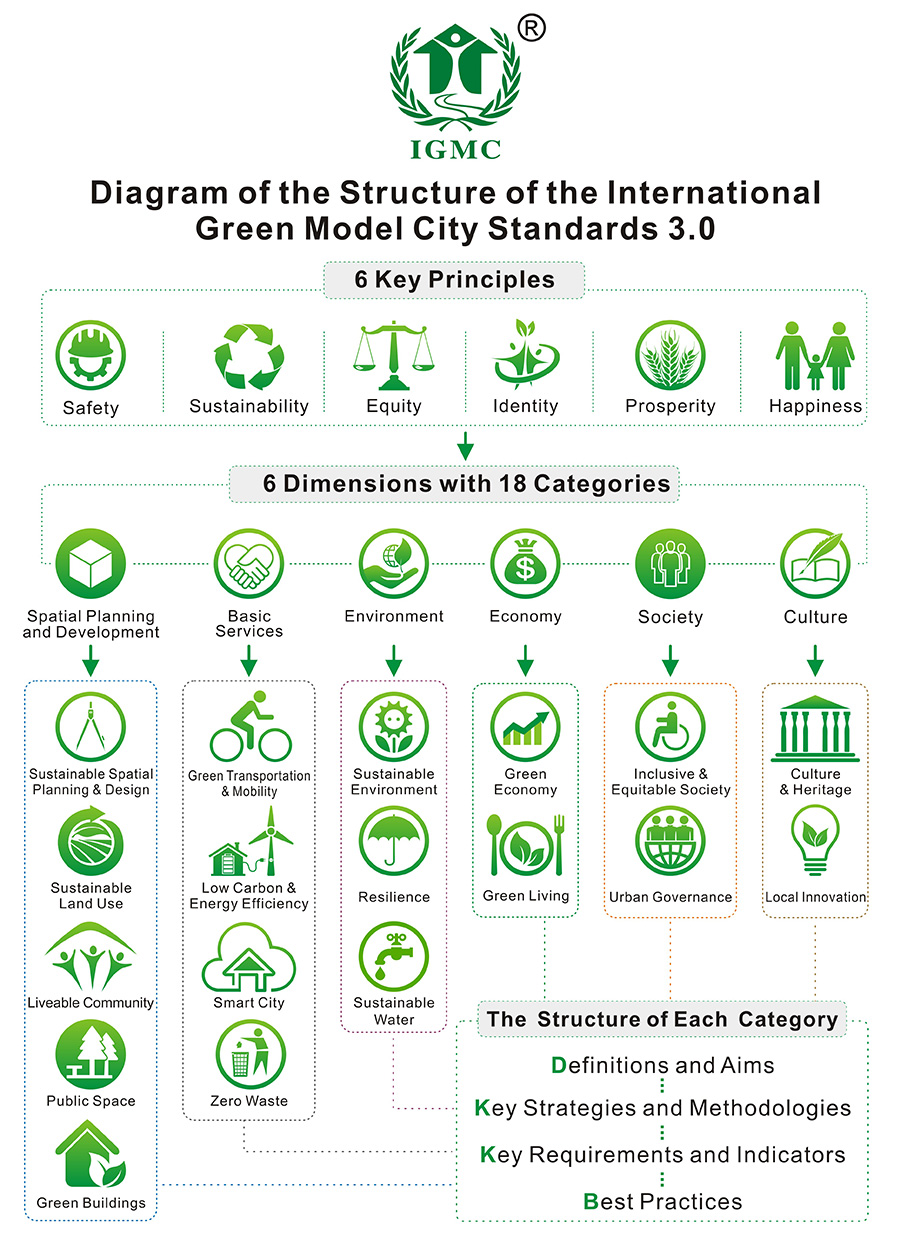
The vision of the IGMC 3.0 is structured
around 6 Key principles: Safety, Sustainability, Equity, Identity, Prosperity,
and Happiness. These principles are put into action through 18 structural
categories spanning across 6 dimensions including environment, spatial planning
and development, economy, basic services, society, and culture, which are
elaborated in depth through their respective definitions and aims, key
methodologies, key indicators, rating system and best practices.
IGMC 3.0 builds on a more comprehensive
approach of environmental, low-carbon, and resources multiplicative
efficiencies. This cascading approach starts by optimizing spatial planning,
urban form, transportation, thus reducing the demand for energy and resources
at a higher scale and continues by optimizing buildings and systems themselves,
which further reduces the demand and allows demand / supply management to
increase even further efficiency. The actual improvements in energy and
resource productivity of each of these interventions are not simply the sum of
each intervention, but are ‘multiplicative’ if they are implemented in mutually
reinforcing ways.
Aiming at assessing and guiding sustainable
urban development for both new and existing urban areas, the main functions and
benefits of IGMC 3.0 include:
1. Guiding the overall process of urban
sustainable development projects based on transit orientation and integrated
planning by providing innovative concepts, integrated strategies and
methodologies, benchmarks and monitoring framework for improved overall
performance and efficient investment.
2. Appraising projects at planning or
design phases to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement, avoiding
various risks.
3. Assessing efficiency, inclusiveness,
sustainability, and resilience of existing urban areas for comparison with
others and to identify opportunities for improvement and transition to more
sustainable cities and human settlements for all.
4. Providing the basis for decision-making
from multi-scale levels of government especially from metropolitan and
city-wide polices to strategies of sub-city districts and communities,
promoting implementation of SDGs and New Urban Agenda through formulation of
action plans and policy recommendations.
5. Providing a timely urban sustainable
development manual for training for relevant stakeholders including mayors,
urban managers, developers, planners, architects and engineers.
The rating system with around 100
indicators is calibrated on UN Habitat, UNEP, and GEF recommendations, and on
benchmarks of best practice. In general, the indicators, benchmarks, and
distribution of points aim to:
1. Reflect a general consensus among
international organizations, academics and practitioners on the aspects of
urban planning, design and policy that have the greatest impact on fostering
greener economic growth and social inclusiveness while reducing carbon
emissions and environmental pressure.
2. Reward decisions made by the project
team, to proactively drive project implementation toward a transformative
sustainable urban development.
3. Be easily applicable, based on
information that can be readily obtained, used and easy to verify
independently.
4. Be relevant to a wide range of urban
development projects in different contexts.
In principle, the scope of application of
the IGMC pilot projects ranges from an integrated area of a land coverage from
750 mu (50 ha) to a wider size and varieties of cities, towns, districts,
communities, neighbourhood and other applicative urban development projects.
There are three types of IGMC pilots: New
projects import IGMC standards from site selection; Ongoing projects import
IGMC standards; Urban renewal projects import IGMC standards from the
beginning.
Welcome to register in IGMC 3.0. For more information please don’t hesitate to contact us.
IGMC Assessment system